About Us
Noavaran Tahghigh engineering company was established in 1995 with the purpose of working in the field of preparation, distribution and sale of different communication and educational software and hardware. Noavaran Tahghigh now has more than 27 years of experience in working and cooperating with 10,000 governmental and private organizations.
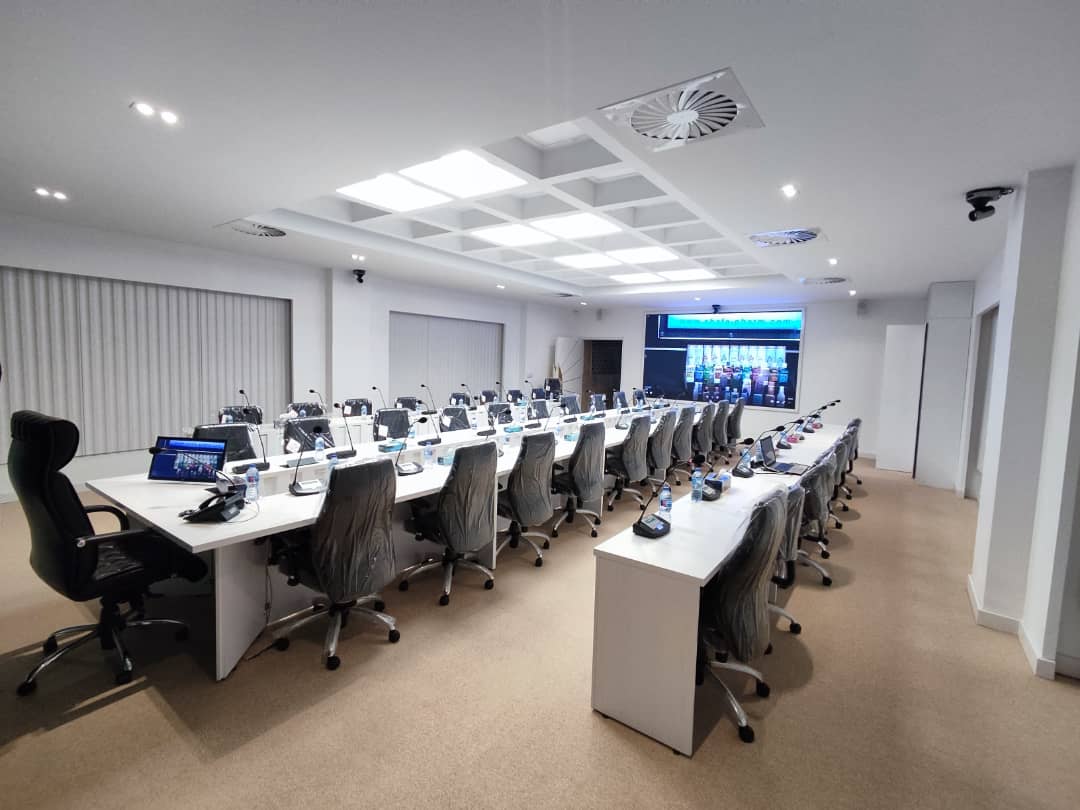

Conference Microphones
Video Wall
Webcams
Conference Cam
Monitors
Our Services
In Novaran Research Company, technical services are considered as a very vital and fundamental part of the company. Our technical team includes the best specialists and experts who have the ability to provide advanced and professional services to customers with great experience and technical knowledge.
Equipment Installation
Equipment repair
Download Center
Warranty Activation
Brands
The products of Navavaran Research Company are recognized as leading brands in the industry by applying advanced technologies and paying attention to unique details and precision in production. Relying on an experienced and expert team, Novaran Research Engineering Company has always tried to meet the needs and expectations of its customers in the best possible way. The exceptional performance and high quality of the products and services offered by these brands have made them a top choice.